Foot & Ankle
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome (TTS) occurs when the posterior tibial nerve in the foot is compressed as it passes through the tarsal tunnel. This condition is similar to carpal tunnel syndrome in the wrist, where pressure on the nerve causes a variety of symptoms, including pain, numbness, and tingling. TTS can affect daily activities and lead to chronic discomfort if left untreated.
What is Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome?
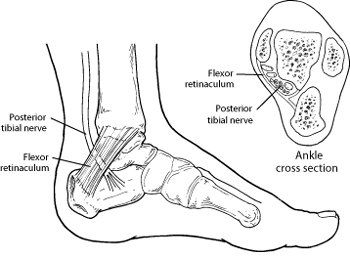
The tarsal tunnel is a narrow space located on the inside of the ankle, formed by the bones of the foot and covered by a tough fibrous tissue. Within this tunnel, the posterior tibial nerve, along with tendons and blood vessels, travels to the foot. When the tibial nerve becomes compressed or pinched, it leads to Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome, causing a range of symptoms that affect the foot and ankle.
Symptoms of Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
The most common symptoms of TTS include:
- Pain: A sharp or burning pain in the foot, especially in the arch, heel, or sole.
- Numbness and Tingling: A sensation similar to an electric shock, often felt in the bottom of the foot or heel.
- Burning Sensation: Many patients report a feeling of burning along the inside of the ankle and foot.
- Radiating Pain: Pain may extend from the ankle to the toes, especially when standing or walking for long periods.
- These symptoms tend to worsen with activity and may be aggravated by walking or standing, especially for extended periods.
Causes of Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome is primarily caused by compression of the posterior tibial nerve. Several factors can contribute to this nerve compression, including:
- Foot Deformities: Conditions like flat feet (fallen arches) can lead to abnormal foot mechanics and increase the pressure on the tibial nerve.
- Trauma or Injury: Fractures, sprains, or dislocations of the ankle may cause scar tissue or swelling that compresses the nerve.
- Bone Spurs or Ganglions: Abnormal bone growth (bone spurs) or benign cysts (ganglions) can press against the nerve in the tarsal tunnel.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like arthritis, diabetes, and vascular diseases can cause swelling and inflammation, further compressing the tibial nerve.
- Abnormal Blood Vessel Growth: Abnormal blood vessel formation (angiomas) can contribute to nerve compression.
Diagnosis of Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
To diagnose TTS, a healthcare provider will conduct a thorough physical examination and consider the patient's medical history. Specific tests include:
- Tinel’s Test: This involves tapping the posterior tibial nerve to check for pain or tingling sensations, which are indicative of TTS.
- Imaging Studies: X-rays, MRI, or CT scans may be ordered to rule out other conditions such as fractures or tumours.
- Nerve Conduction Studies (EMG/NCV): If necessary, electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction velocity (NCV) tests can be performed to assess nerve function and determine the extent of nerve damage.
Treatment Options for Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
Treatment for TTS typically begins with non-operative methods. If these approaches are ineffective, surgery may be required.
Non-Operative Treatments for TTS
- Orthotics and Footwear: Specially designed shoe inserts or braces help support the arch of the foot, reducing pressure on the tibial nerve. Wearing shoes with proper arch support is essential.
- Anti-inflammatory Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or paracetamol, can help relieve pain and reduce swelling in the foot.
- Corticosteroid Injections: Steroid injections may be used to reduce inflammation and provide temporary pain relief.
- Rest and Ice Therapy: Resting the affected foot and applying ice packs for 15–20 minutes a few times a day can help reduce swelling and manage pain.
Surgical Treatment for TTS
In cases where non-surgical treatments do not provide relief, surgery may be necessary. Surgical options include:
- Tarsal Tunnel Release Surgery: This procedure involves making an incision to open the tarsal tunnel and release the pressure on the tibial nerve. The surgeon may remove any tissue, bone spurs, or cysts that may be contributing to the nerve compression.
Why Choose Dr. Ryan du Sart for Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment?
Dr. Ryan du Sart is an experienced orthopaedic surgeon who specialises in foot and ankle conditions, including Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome. His expertise in both non-surgical and surgical treatment options ensures that patients receive the best possible care tailored to their needs.
Book a Consultation
If you are experiencing symptoms of Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome, early intervention is crucial to prevent long-term nerve damage. Contact Dr. Ryan du Sart for a consultation to discuss your treatment options and get back on the path to pain-free movement.
Phone: (08) 9779 9767
Email:
admin@ryandusart.com.au
Locations:
6 Higgins Street, South Bunbury, WA 6230
20 Prince Street, Busselton, WA 6280
References:
- Zhao, C., & Zhang, L. (2018). "Diagnosis and Management of Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome." Foot & Ankle International, 39(6), 751-759.
- Jones, K., & O’Neill, J. (2020). "Surgical Outcomes of Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome: A Comprehensive Review." Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research, 15(1), 14-21.
- Smith, T., & Barrios, A. (2021). "Non-Surgical Management of Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome: A Review of Conservative Treatment Modalities." Foot and Ankle Clinics, 26(2), 305-315.

