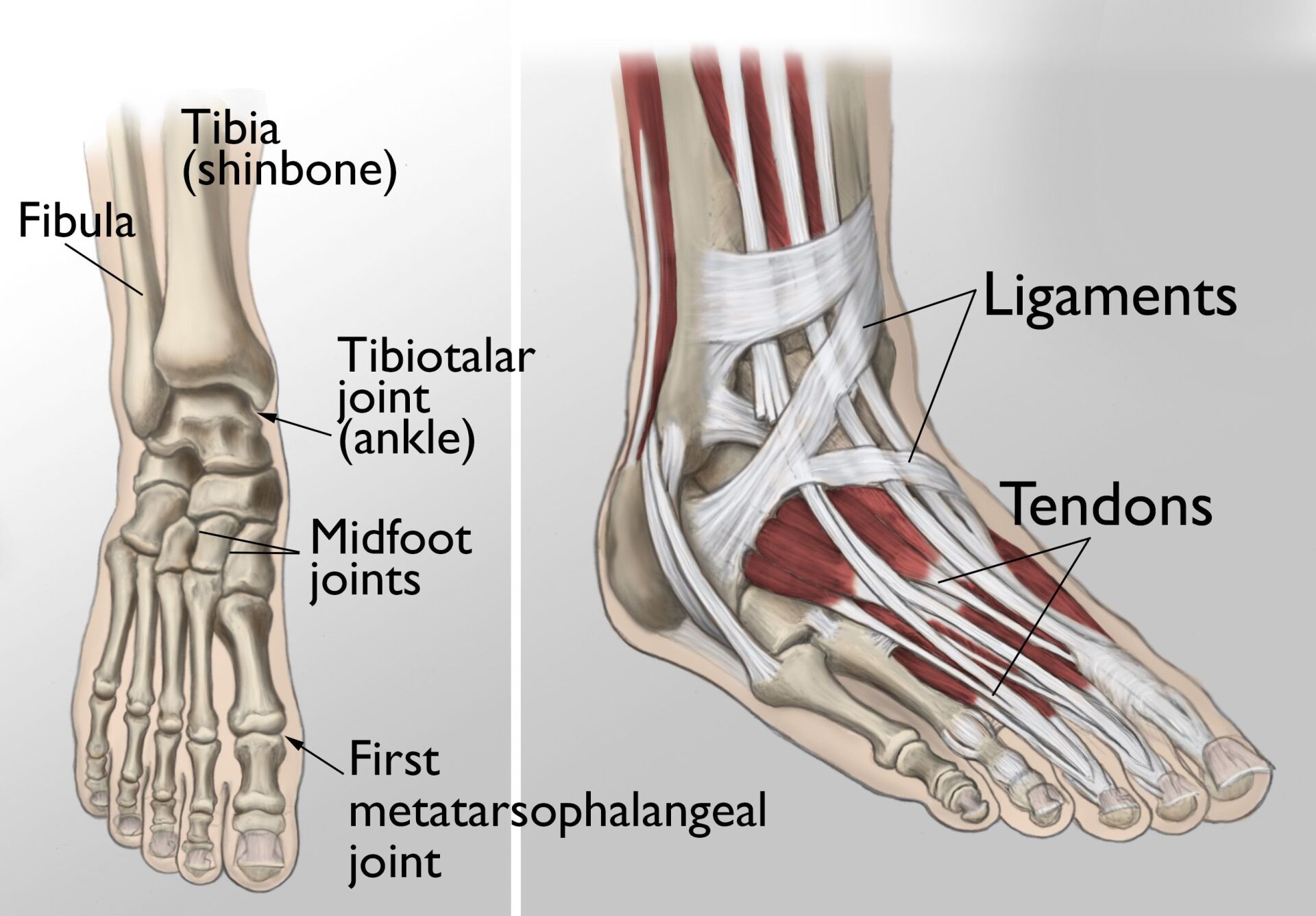
Foot & Ankle
Foot & Ankle Arthritis
Foot and ankle arthritis is a degenerative condition that primarily affects the joints in the ankle, midfoot, and big toe. It is typically a result of prior trauma to the region but can also arise from autoimmune or inflammatory conditions. Over time, arthritis leads to pain, swelling, and restricted movement, often resulting in joint deformities.
Types of Foot & Ankle Arthritis
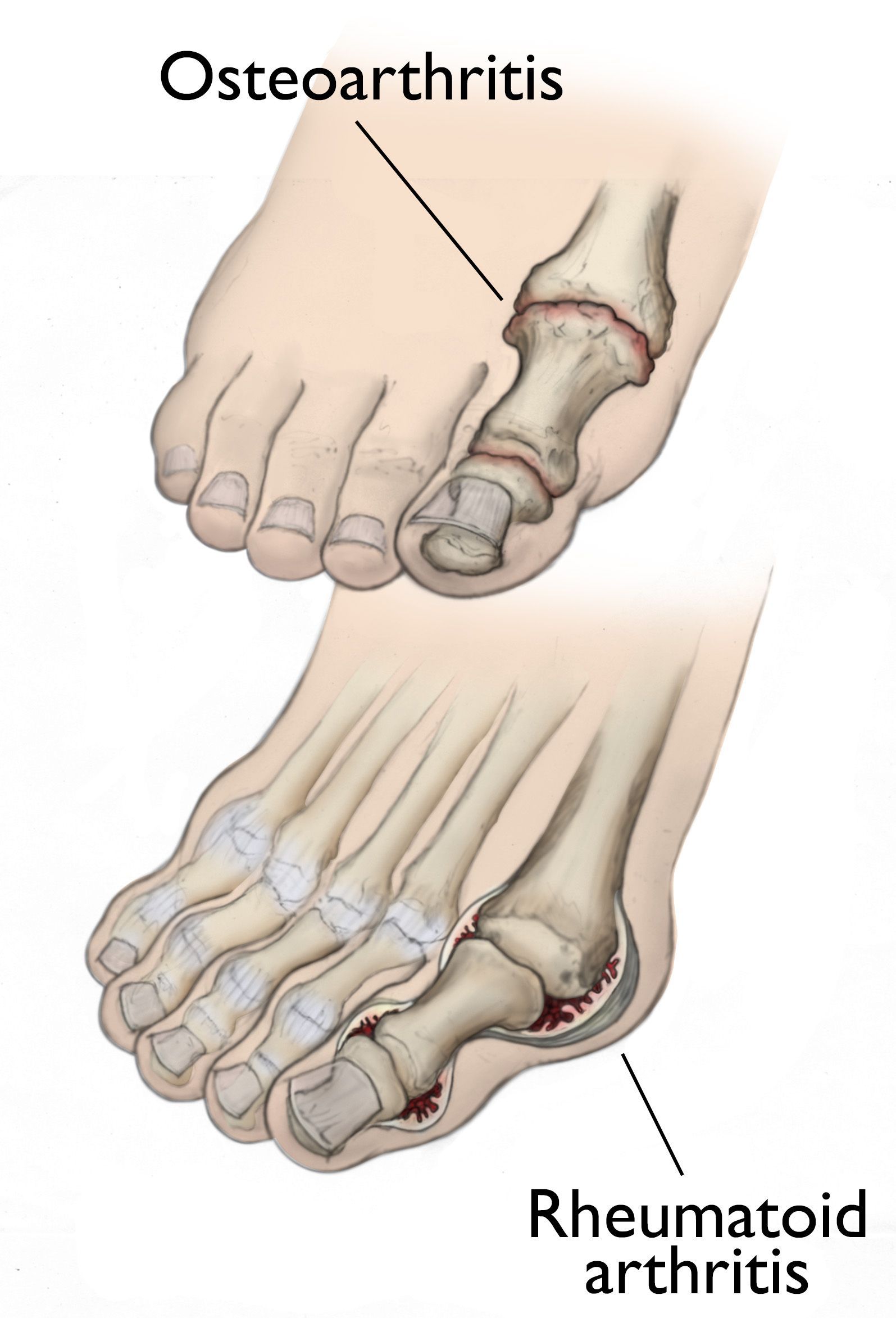
1. Osteoarthritis (Degenerative Joint Disease)
- The most common form of arthritis, osteoarthritis often affects older individuals.
- It begins with cartilage breakdown, which cushions the bones in the joint, leading to bone-on-bone contact as the cartilage deteriorates.
- In severe cases, bone spurs (bony growths) may form around the joint, causing further discomfort and limited mobility.
2. Rheumatoid Arthritis
- An autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks healthy joints, including those in the feet and ankles.
- Rheumatoid arthritis causes pain, stiffness, swelling, and loss of joint function, often affecting both sides of the body symmetrically (e.g., both ankles or both feet).
- Inflammation from this condition can result in severe damage to the affected joints if untreated.
3. Post-Traumatic Arthritis
- This type develops after a previous trauma or injury, such as a fracture, severe sprain, or ligament tear.
- The trauma can lead to joint instability, cartilage damage, and long-term wear on the affected joint, leading to arthritis years after the initial injury.
Symptoms of Foot and Ankle Arthritis
Symptoms of foot and ankle arthritis vary depending on the specific joint affected. Common symptoms include:
- Pain that worsens with movement or activity.
- Tenderness when pressure is applied to the joint.
- Swelling, often accompanied by warmth and redness.
- Reduced range of motion, making it difficult to walk or perform daily activities.
- Increased pain during vigorous activity or when walking on hard surfaces.
As arthritis progresses, joint deformities may develop, further limiting the function and mobility of the foot and ankle.
Causes of Foot and Ankle Arthritis
The causes of foot and ankle arthritis depend on the type of arthritis present:
- Osteoarthritis is typically caused by wear and tear on the joints over time, worsened by previous injuries, joint overuse, or ageing.
- Rheumatoid arthritis arises from autoimmune attacks on healthy tissues, including cartilage and synovial membranes.
- Post-traumatic arthritis is caused by injuries such as fractures, dislocations, or ligament tears that result in long-term joint damage.
Other contributing factors may include:
- Congenital deformities or abnormal joint structure.
- Obesity, which places excess stress on the joints.
- Previous infections or inflammatory diseases like gout or psoriasis.
Diagnosis of Foot and Ankle Arthritis
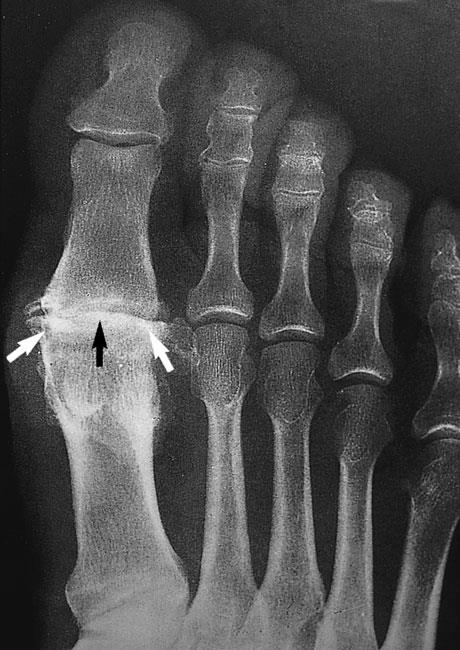
Diagnosis of foot and ankle arthritis typically begins with a comprehensive medical consultation and physical examination to evaluate joint function, tenderness, and swelling. Common diagnostic tools include:
- X-rays to assess bone changes, joint space narrowing, and the presence of bone spurs.
- MRI or CT scans to evaluate cartilage, ligaments, and tendons, and to rule out other possible causes of pain.
Treatment Options for Foot and Ankle Arthritis
Non-Operative Treatments
The first-line treatment for foot and ankle arthritis usually focuses on pain management and preserving joint function:
- Painkillers like paracetamol and NSAIDs (anti-inflammatory drugs).
- Physical therapy to improve range of motion and strengthen the muscles around the joint.
- Assistive devices, such as ankle-foot orthoses (AFOs), orthotics, and custom-made shoes to alleviate pressure on the joint and reduce pain.
- Lifestyle modifications: Weight loss, avoiding high-impact activities, and transitioning to low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling to reduce stress on the joints.
Surgical Treatments
If arthritis progresses and non-surgical treatments fail, surgical intervention may be considered:
- Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive surgery to clean out damaged tissue, remove bone spurs, or debride the joint. This technique can provide relief but does not cure arthritis.
- Ankle Fusion (Arthrodesis): In cases of severe arthritis, ankle fusion surgery may be required to permanently join the bones of the ankle, eliminating movement in the joint but providing pain relief.
- Total Ankle Replacement (TAR): In this procedure, the damaged cartilage and bone are replaced with metal and plastic implants, restoring normal function and alleviating pain. TAR is recommended when the joint is severely damaged by osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or post-traumatic arthritis.
Post-Surgery Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery after foot and ankle surgery depends on the type of procedure performed:
- For ankle fusion, patients will need to limit weight-bearing for several weeks, and a walking boot may be worn for stability.
- Physical therapy will be essential to regain mobility, improve strength, and reduce swelling.
- For total ankle replacement, recovery times vary, but patients can expect to gradually return to weight-bearing activities within 6 to 12 months.
Why Choose Dr. Ryan du Sart?
Dr. Ryan du Sart is a fellowship-trained orthopaedic surgeon with extensive experience in diagnosing and treating foot and ankle arthritis. Whether through non-surgical methods or advanced surgical interventions, Dr. du Sart offers a comprehensive approach to managing arthritis and restoring function in the foot and ankle.
Book a Consultation
If you are experiencing foot and ankle pain or symptoms of arthritis, early intervention can help prevent long-term complications and improve your quality of life. Book a consultation with Dr. Ryan du Sart today to discuss your treatment options.
Phone: (08) 9779 9767
Email: admin@ryandusart.com.au
Locations:
6 Higgins Street, South Bunbury, WA 6230
20 Prince Street, Busselton, WA 6280
References:
- Michaud, T. L., et al. (2021). "Management of Foot and Ankle Arthritis." Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 29(5), e173-e181.
- Davis, W. H., & Bray, C. P. (2019). "Total Ankle Replacement: A Review." Orthopaedic Clinics of North America, 50(1), 119-126.
- Barker, L., et al. (2018). "Arthritis and its Management: A Comprehensive Overview of Current and Emerging Therapies." Rheumatology and Therapy, 5(2), 123-134.

