FOOT & ANKLE
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction
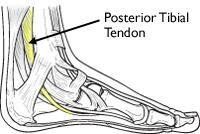
The Posterior Tibial Tendon passes through the ankle to attach the calf muscle with the bones of the mid foot. It provides stability to the arch and supports the foot while walking. Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the tendon becomes inflamed or torn causing dysfunction, pain and the development of flatfoot.
Symptoms
Symptoms of Posterior Tibial Tendon dysfunction include:
- Pain on the inside of the foot and ankle which may be accompanied by swelling
- Pain that increases with activity. High impact/intensity activities can be difficult and some people have trouble walking or standing for long periods.
- Pain on the outside of the ankle. When the foot collapses, the heel bone may shift to a new position outwards. This can put pressure on the outside ankle bone.
Causes
An acute injury, such as a fall, can tear the posterior tibial tendon or cause it to become inflamed. Overuse for example from high impact sports can also be a cause. Once the tendon becomes inflamed or torn, the arch will slowly fall (collapse) over time. Additional risk factors include obesity, diabetes, and hypertension.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made by medical consultation, taking the patient's past medical history and examination testing for pain, changes in ankle position ,flexibility, strength and range of motion. X-ray, MRI, CT or ultrasound scans may be requested to visualise the tendon and rule out other abnormalities.
Treatment Options
Non Operative Treatment
Initial non operative treatment measures include rest, regular application of ice to reduce inflammation, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medication, steroid injection where indicated, immobilisation with a case or walking boot, orthotics or braces, shoe inserts to support the arch and physical therapy to strengthen the tendon.
Surgery
If pain does not improve with non operative treatment, surgery may be recommended. The type of surgery depends on where tendonitis is located and how much the tendon is damaged.
Surgical options include:
- Tenosynovectomy - The inflamed tendon tissue is cleaned and removed
- Tendon transfer - Damaged tendon is replaced by another foot tendon
- Arthrodesis - In cases where arthritis has developed, the bones are realigned and fused to form a single bone by removing cartilage.
- Osteotomy - Bones of the heel and midfoot ay be cut to create the arch of the foot

© All rights reserved
For all appointments and enquiries please contact us on:
Phone: 08 9779 9767
Email: admin@ryandusart.com.au
Address: 6 Higgins St, South Bunbury, 6230
